In the ever-evolving world of civil engineering and infrastructure development, geosynthetics have become indispensable materials for solving complex geotechnical challenges. From soil stabilization and erosion control to drainage and containment, these synthetic materials are shaping the future of sustainable construction. In this blog, we explore the classification of geosynthetics, explain the functions of each type, and highlight how they are transforming projects around the world.
At Prime Terratech Industries Pvt. Ltd., we specialize in supplying a wide range of high-quality geosynthetic products tailored for infrastructure, environmental, and geotechnical applications.
What Are Geosynthetics?
Geosynthetics refer to synthetic materials—typically made from polymers like polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), or high-density polyethylene (HDPE)—used in contact with soil, rock, or earth materials for a wide range of civil engineering functions. These include separation, filtration, reinforcement, drainage, and containment.
First introduced in the 1960s, geosynthetics have revolutionized construction techniques across highways, railways, landfills, mining sites, and hydraulic structures. Today, they are an essential component of both temporary and permanent infrastructure solutions.
Types of Geosynthetics and Their Applications
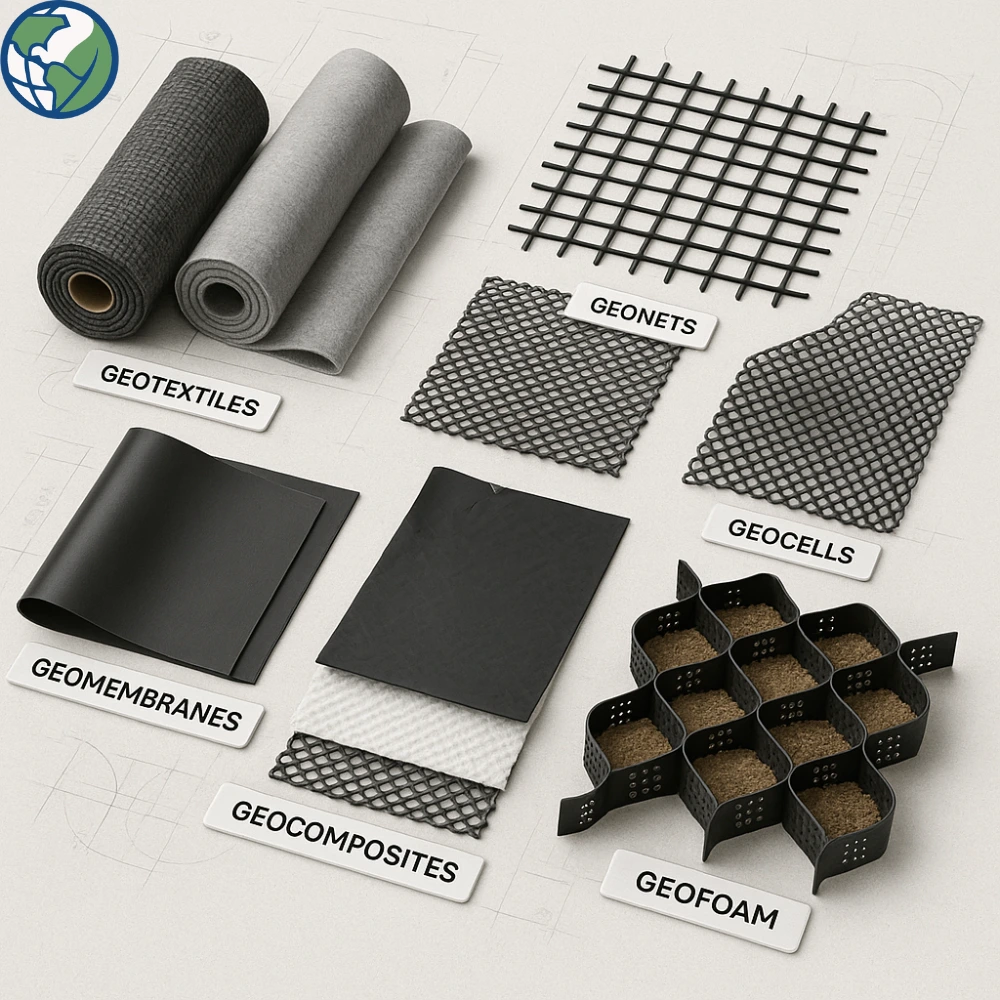
1. Geotextiles
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics made from synthetic fibers. They come in two main types: woven and non-woven.
- Woven geotextiles offer high tensile strength and are ideal for soil reinforcement and separation applications.
- Non-woven geotextiles are typically used for filtration, drainage, and erosion control.
Applications:
- Road and railway subgrade separation
- Drainage systems
- Landfill lining protection
- Riverbank and coastal erosion prevention
At Prime Terratech Industries Pvt. Ltd., our geotextiles are engineered to meet performance standards for both load-bearing and filtration efficiency.
2. Geogrids
Geogrids are grid-like structures formed by stretching polymer sheets or joining rods to create apertures. They provide strong tensile reinforcement to soils.
- Uniaxial geogrids offer strength in one direction and are used in retaining walls and slopes.
- Biaxial geogrids provide reinforcement in two directions, ideal for base stabilization.
Applications:
- Reinforcement of retaining walls
- Load distribution on weak subgrades
- Embankment stabilization
- Airport runway construction
3. Geonets
Geonets are made by extruding two or more polymer layers that intersect at an angle to form a net-like structure. They are primarily used for drainage.
Applications:
- Landfill leachate drainage
- Retaining wall back drainage
- Tunnel and bridge waterproofing systems
Unlike geotextiles, geonets allow for high in-plane water flow and are often used beneath geomembranes or in geocomposite layers.
4. Geomembranes
Geomembranes are impermeable sheets made from polymers like HDPE or PVC, used to prevent fluid migration.
Applications:
- Canal and reservoir liners
- Waste containment in landfills
- Mining leachate ponds
- Chemical containment basins
Geomembranes act as barrier systems and are often used in combination with other geosynthetic materials like geotextiles or geonets for added protection.
5. Geocomposites
Geocomposites are multi-functional geosynthetic products that combine two or more components (e.g., geotextile + geonet or geomembrane + geogrid) to meet specific engineering demands.
Applications:
- Vertical and horizontal drainage
- Gas collection in landfills
- Roadway drainage
- Waterproofing in tunnels
These hybrid systems provide combined benefits such as filtration + drainage or containment + reinforcement, streamlining project execution.
6. Geocells
Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures made from HDPE strips. Once expanded and filled with soil or aggregates, they create a stable mattress-like layer that distributes loads and prevents erosion.
Applications:
- Slope stabilization
- Load support for pavements and access roads
- Shoreline protection
- Channel and embankment lining
7. Other Geosynthetics
Additional products include:
- Geofoam: Lightweight expanded polystyrene blocks used for embankments or backfill
- Geobags: Filled with soil or sand, used for erosion control and temporary structures
Choosing the Right Geosynthetic Product
Selecting the appropriate geosynthetic depends on several factors:
- Function (e.g., reinforcement, drainage, separation)
- Site conditions (soil type, slope, water table)
- Load-bearing requirements
- Environmental considerations
At Prime Terratech Industries Pvt. Ltd., our technical team helps clients choose the right solution through site assessment and performance-based design.
Conclusion
Geosynthetics are redefining how we build, stabilize, and protect infrastructure in the 21st century. From geotextiles and geogrids to geomembranes, geonets, and geocells, these materials offer durability, cost-efficiency, and environmental sustainability across a wide range of engineering applications.
With decades of experience, Prime Terratech Industries Pvt. Ltd. provides engineered geosynthetic solutions trusted by contractors, civil engineers, and infrastructure developers across India and international markets.
Whether you’re constructing a highway, stabilizing a slope, lining a landfill, or managing stormwater, geosynthetics are the backbone of modern geotechnical innovation. Contact us today to learn more about how our geosynthetic systems can enhance the performance and longevity of your next project.